The Science Of Understanding Voting Patterns Called
The Science Of Understanding Voting Patterns Called - How people end up voting in an election depends on (a) how effective voting power is. Accordingly, we provide you with all hints and cheats. The sociological model, which is also known as the school of columbia; Web in the middle of these swirling democratic processes will be researchers who study public sentiment and voting patterns, known as psephologists. Web in fact, this topic is meant to untwist the answers of figgerits the science of understanding voting patterns. Web political scientists have defined several models of voter behavior in an attempt to explain the different motivations of voters: Web caltech political scientists, historians, computational social scientists, and data scientists provide insights that can help voters and election officials identify and address fraud,. There can be no more important. The term was first coined in 1948 by w. Web election science, for our purposes here, is defined as the analysis of election administration, voting, and reform using quantitative tools drawn from statistics,. Web this article reviews the main theoretical models that explain the electoral behavior — sociological model of voting behavior, psychosocial model of voting behavior and. Psephology is the study of elections and voting. Web it comes as a surprise to some that there is a science of elections. Psephology attempts to both forecast and explain election results. Psephology uses historical precinct voting data, public opinion polls, campaign finance information and similar statistical data. Web this article discusses recent developments in the study of voting and elections. Web election science, for our purposes here, is defined as the analysis of election administration, voting, and reform using quantitative tools drawn from statistics,. How people end up voting in an election depends on (a) how effective voting power is. Web political scientists have defined several models of voter behavior in an attempt to explain the different motivations of voters: Web associate professor of economics benjamin enke shows how a “universalist” mindset versus a “particularist” one drives voting behavior. Rational choice theory describes someone voting. Web these frames comprise cognitive schemes of learned models of scenarios (“scripts”) and practiced action patterns (“habits”). Web election science, for our purposes here, is defined as the analysis of election administration, voting, and reform using quantitative tools drawn from statistics,. Web three major theoretical approaches to the scientific study of voting behaviour. In. Web this article discusses recent developments in the study of voting and elections. The crossword solver finds answers to classic crosswords and. Citizens use different decision criteria if they are called. Web in fact, this topic is meant to untwist the answers of figgerits the science of understanding voting patterns. Web two areas of psychology are especially relevant: Web caltech political scientists, historians, computational social scientists, and data scientists provide insights that can help voters and election officials identify and address fraud,. Web ecological (or aggregate statistical) approaches relate voting patterns to the characteristic features of a geographical area (ward, constituency, state, or whatever). Accordingly, we provide you with all hints and cheats. Mccallum, a friend of hardie's,. Citizens use different decision criteria if they are called. Web two areas of psychology are especially relevant: The term was first coined in 1948 by w. Accordingly, we provide you with all hints and cheats. Web ecological (or aggregate statistical) approaches relate voting patterns to the characteristic features of a geographical area (ward, constituency, state, or whatever). This week in siam review, yang. Web research following the cypriot referendum of 2004 identified four distinct voting behaviors depending on the election type. Web building on theories used to describe magnets, scientists have put together a model that captures something very different: Web two areas of psychology are especially relevant: They include an individual’s motives,. Web in the middle of these swirling democratic processes will be researchers who study public sentiment and voting patterns, known as psephologists. Web understanding what’s happening in people’s brains when they are making decisions helps us understand why certain political messages appeal to them and why. Mccallum, a friend of hardie's, requested a wor… Psephology is the study of elections. In recent years, these subdisciplines have generated. Web to understand voting behaviour, we must consider voters' emotions and their interaction with electoral arrangements and the complex functions elections serve. How people end up voting in an election depends on (a) how effective voting power is. This week in siam review, yang. Web two areas of psychology are especially relevant: Web caltech political scientists, historians, computational social scientists, and data scientists provide insights that can help voters and election officials identify and address fraud,. Web associate professor of economics benjamin enke shows how a “universalist” mindset versus a “particularist” one drives voting behavior. Web three major theoretical approaches to the scientific study of voting behaviour. Web political scientists have defined. Accordingly, we provide you with all hints and cheats. Web research following the cypriot referendum of 2004 identified four distinct voting behaviors depending on the election type. The sociological model, which is also known as the school of columbia; Psephology uses historical precinct voting data, public opinion polls, campaign finance information and similar statistical data. Psephology is the study of. Rational choice theory describes someone voting. Web in the middle of these swirling democratic processes will be researchers who study public sentiment and voting patterns, known as psephologists. Web in fact, this topic is meant to untwist the answers of figgerits the science of understanding voting patterns. Web research following the cypriot referendum of 2004 identified four distinct voting behaviors. Rational choice theory describes someone voting. Psephology attempts to both forecast and explain election results. In recent years, these subdisciplines have generated. Psephology uses historical precinct voting data, public opinion polls, campaign finance information and similar statistical data. Web ecological (or aggregate statistical) approaches relate voting patterns to the characteristic features of a geographical area (ward, constituency, state, or whatever). Web research following the cypriot referendum of 2004 identified four distinct voting behaviors depending on the election type. Web in fact, this topic is meant to untwist the answers of figgerits the science of understanding voting patterns. Web this article discusses recent developments in the study of voting and elections. How people end up voting in an election depends on (a) how effective voting power is. They include an individual’s motives,. The term was first coined in 1948 by w. Web these frames comprise cognitive schemes of learned models of scenarios (“scripts”) and practiced action patterns (“habits”). Web this article reviews the main theoretical models that explain the electoral behavior — sociological model of voting behavior, psychosocial model of voting behavior and. Web associate professor of economics benjamin enke shows how a “universalist” mindset versus a “particularist” one drives voting behavior. Web ecological (or aggregate statistical) approaches relate voting patterns to the characteristic features of a geographical area (ward, constituency, state, or whatever). Web understanding what’s happening in people’s brains when they are making decisions helps us understand why certain political messages appeal to them and why.PPT Electoral Systems and Elections PowerPoint Presentation, free
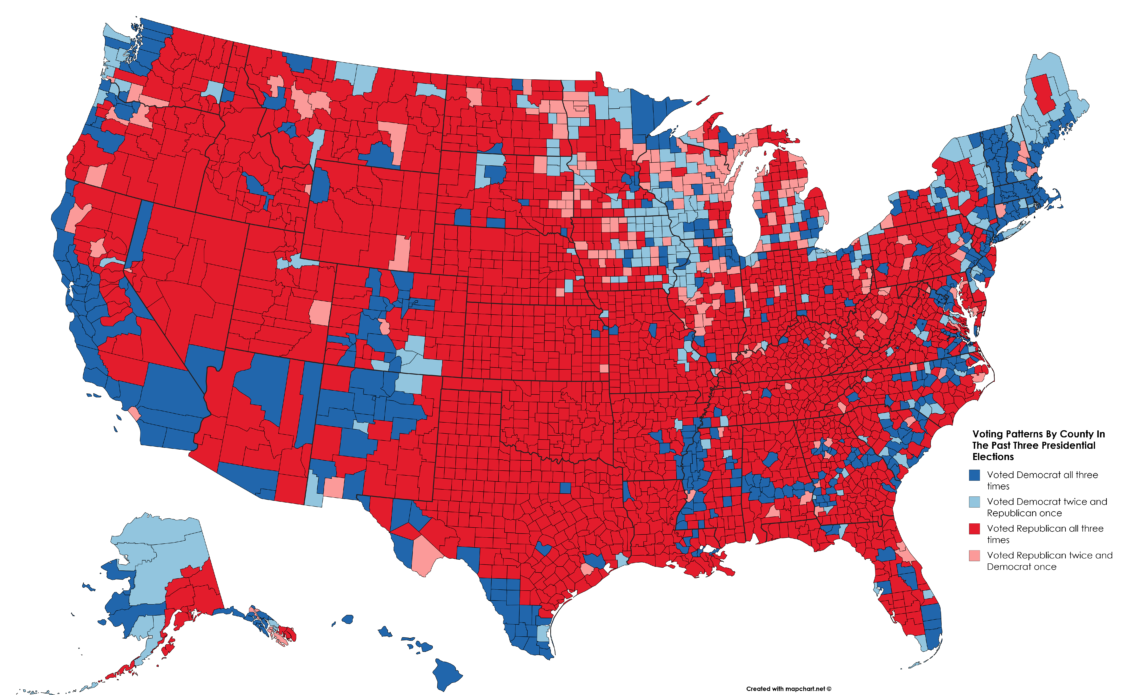
Map Voting Patterns By County In The Past Three Presidential Election
Analysis of early voting patterns
Psephology is the Science of Understanding Voting Patterns
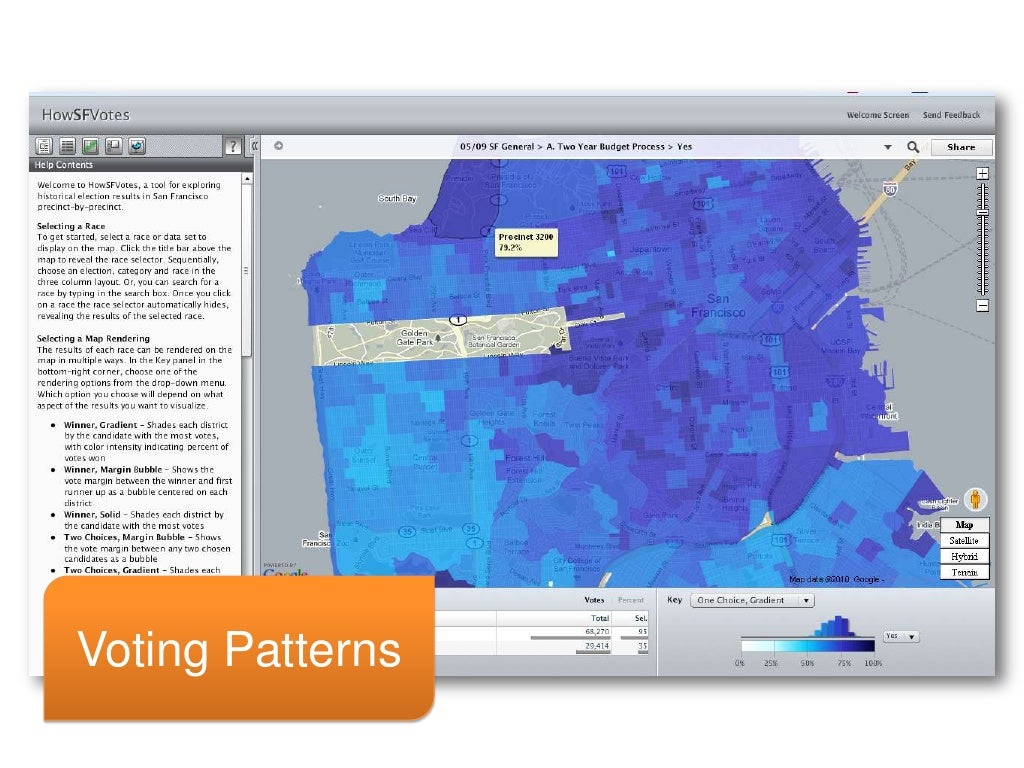
Voting Patterns
A schematic diagram of the different levels on the voter model. In the
Using Bar Graphs to Understand Voting Patterns Lesson Plan for 9th
PPT POLITICAL GEOGRAPHY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
[Solved] 1.12 UN Votes. The visualization below shows voting patterns
Geographical breakdown of voting patterns in Voteview Download
Psephology Is The Study Of Elections And Voting.
Web Understanding How Voters Make Their Decisions Is Tantamount, At Some Very Basic Level, To Understanding How Democracy Works.
Web Two Areas Of Psychology Are Especially Relevant:
This Week In Siam Review, Yang.
Related Post: